Magnesium: foods, functions, how much do you need & more
Last Updated : 11 January 2021Magnesium is often associated with supporting the proper functioning of our muscles. However, this mineral has more than 300 other roles that are equally important for our bodies!
What is magnesium?
Magnesium is one of the major minerals, which our bodies need in relatively large amounts to keep healthy. We can find magnesium in many animal- and plant-based foods, as well as in drinking water.
What are the functions of magnesium?
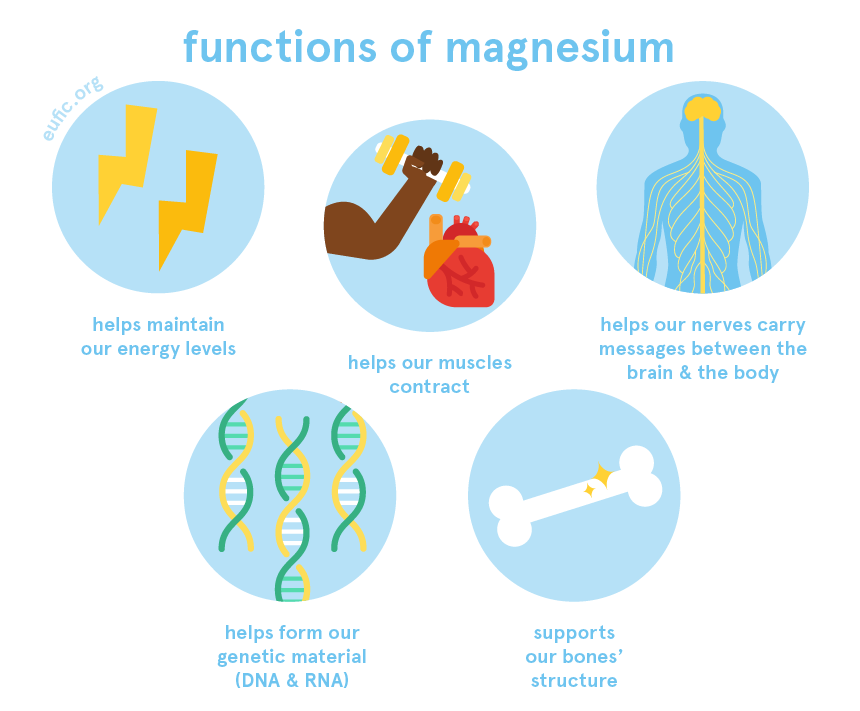
A great part of the magnesium in our bodies is found in our bones, where it supports their structure. The remaining is involved in more than 300 metabolic reactions; via activating or producing different enzymes that otherwise would not function.
One of the key roles of magnesium is to make sure that our cells have enough energy to perform their roles. Besides, magnesium keeps the normal functioning of our cardiovascular and nervous systems by helping nerve cells carry messages (nerve impulses) between the brain and the body, particularly those involved in muscle and heart contraction. This mineral is also needed to help form our genetic material (DNA and RNA).
How much magnesium do I need per day?
How much magnesium you need per day changes according to your age, sex and life-stage.
The dietary reference value (DRV)* for healthy adults (over the age of 18), including during pregnancy and lactation, is between 300-350 mg of magnesium per day.
We can get enough magnesium from our diets by eating a variety of foods. Following your country's dietary guidelines on a healthy and balanced diet will help you meet your needs for magnesium.
* These values are based on the population adequate intake (AI) estimates from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). They should not be interpreted as nutrient goals. To know more about the DRVs in Europe click here.
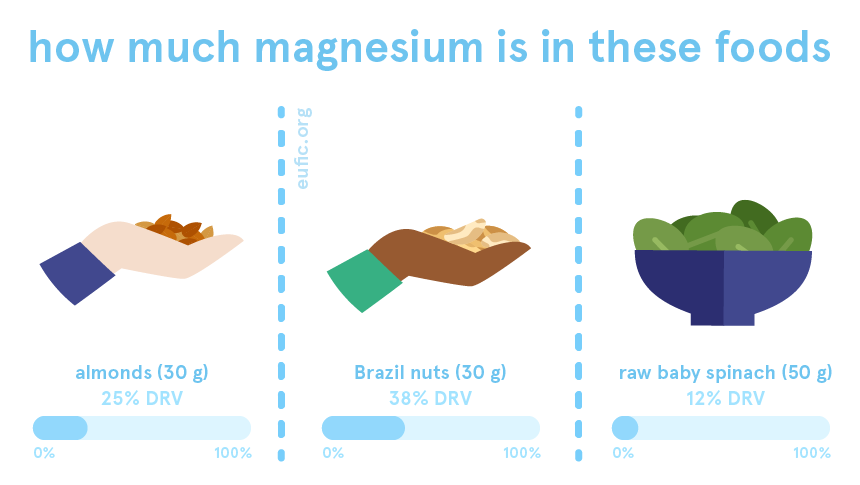
What foods contain magnesium?
Magnesium is found in many foods, as well as in drinking water, though the amount of magnesium in water is usually higher in regions where water has a high mineral content, also called hard water.
Foods rich in magnesium include:
- nuts
- whole grains and grain products
- fish and seafood
- green leafy vegetables
- banana, berries, legumes, berries
- coffee, and some cocoa beverages

Does magnesium interact with other nutrients?
The interactions between magnesium and other nutrients in our diets are still being studied. To this date, no nutrients or compounds seem to impair the absorption or the levels of magnesium in our bodies, in ways that affect our health.
What happens if I have too little magnesium?
Magnesium deficiency is not common since most people can get the recommended amounts of this mineral by eating a varied diet. Magnesium deficiency mainly happens when there are specific conditions, such as kidney or gastrointestinal diseases, that lower the levels of this mineral in our bodies. This can impair any of the functions involving magnesium, but a severe consequence includes the lowering of our levels of potassium, which can lead to heart and neurological problems.
Low levels of magnesium have also been linked with muscle pain, tremors, cramps, and weakness. However, it’s often uncertain if those are a direct consequence of magnesium deficiency or the lack of other nutrients that are also involved in those processes.
What happens if I have too much magnesium?
Magnesium from foods is not considered harmful since it’s very unlikely that we get too much of it through our diet alone.
We do, however, need to be aware of magnesium added to foods or dietary supplements and take no more than 250mg per day on top of our diets.
Before taking magnesium supplements, check with your doctor or a registered dietitian/nutritionist or consult your national dietary guidelines.
When should I pay extra attention to my magnesium intake?
Magnesium deficiency is not a risk for the general population since most people can get the recommended amounts of magnesium from a varied and balanced diet.
References
- European Food Safety Authority. 2015. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for magnesium. EFSA Journal 2015;13(7):4186
- World Health Organization (WHO). 2004. Vitamin and mineral requirements in human nutrition. 2nd edition. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO.
- Public Health England. 2019. McCance and Widdowson’s Composition of Foods Integrated Dataset



