Manganese: foods, functions, how much do you need & more
Last Updated : 11 January 2021‘Manganese’ is derived from the Greek word for ‘magic’, a name that fits a mineral for which there’s still much more to discover!
What is manganese?
Manganese is one of the trace elements, which our bodies only need in small amounts to keep healthy. We can find manganese in a variety of foods, as well as in drinking water.
What are the functions of manganese?
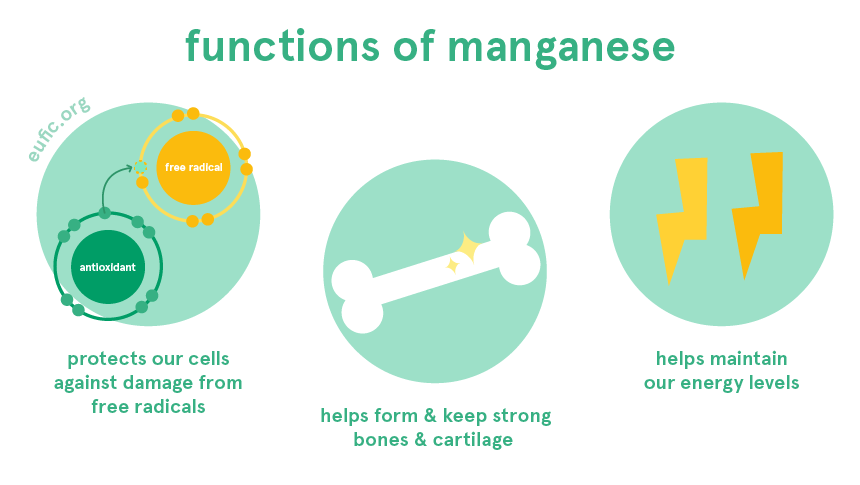
Manganese is needed by different enzymes, which are involved in many bodily functions. For example, manganese is needed to support the metabolism of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates and to help produce our cartilage and bones.
How much manganese do I need per day?
How much manganese you need per day changes according to your age, sex and life-stage.
The dietary reference value (DRV)* for healthy adults (over the age of 18), including during pregnancy and lactation, is 3 mg of manganese a day.
We can get enough manganese from our diets by eating a variety of foods. Following your country's dietary guidelines on a healthy and balanced diet will help you meet your needs for manganese.

* These values are based on the adequate intake (AI) estimates from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). They should not be interpreted as nutrient goals. To know more about DRVs in Europe click here.
What foods contain manganese?
We can find manganese in a variety of foods, as well as in drinking water.
Some of the foods richest in manganese include:
- nuts and seeds
- chocolate
- cereal-based products
- seafood
- pulses
- fruits and fruit products.
Manganese can also be consumed through beverages, such as coffee and tea.

Does Manganese interact with other nutrients?
No nutrients or compounds seem to impair the absorption or the levels of manganese in our bodies, in ways that affect our health.
What happens if I have too little manganese?
Manganese deficiency is rare and little known about. Most people get the recommended amounts of manganese by eating a varied diet since this mineral is widespread in foods and we only need it in very small amounts.
What happens if I have too much manganese?
Manganese from foods is not considered harmful since it’s very unlikely that we get too much of it from foods alone.
Nevertheless, we can still be exposed to toxic amounts of manganese by inhalation (for example in mining work) or through contaminated water. Toxic levels of manganese can cause a permanent neurological disorder called “manganism” which causes serious damage to the nervous system. However, to this date, there’s no maximum safe intake established for manganese due to a lack of scientific studies.
Before taking manganese supplements, check with your doctor or a registered dietitian/nutritionist or consult your national dietary guidelines.
When should I pay extra attention to my manganese intake?
Manganese deficiency is not a risk for the general population since most people can get the recommended amounts of manganese from a varied and balanced diet.
References
- European Food Safety Authority. 2013. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for manganese. EFSA Journal 2013;11(11):3419
- Public Health England. 2019. McCance and Widdowson’s Composition of Foods Integrated Dataset



